Career Guide Evaluative Research
Project Overview
This project focuses on the evaluation of career guide pages that are presented on the WGU pages. The goal of this research is to identify the needs, motivations, and opportunities for product design decisions of WGU career pages. We use usability testing to inform iteration ideas for new prototypes. A/B testing is conducted to compare the conversion rate between the control page and newly-designed prototypes. Follow-up surveys and interviews are utilized to better understand users’ thinking and decision-making process.
My role
Client: Emsi Burning Glass
UX Researcher (Learning Team)
Timeline
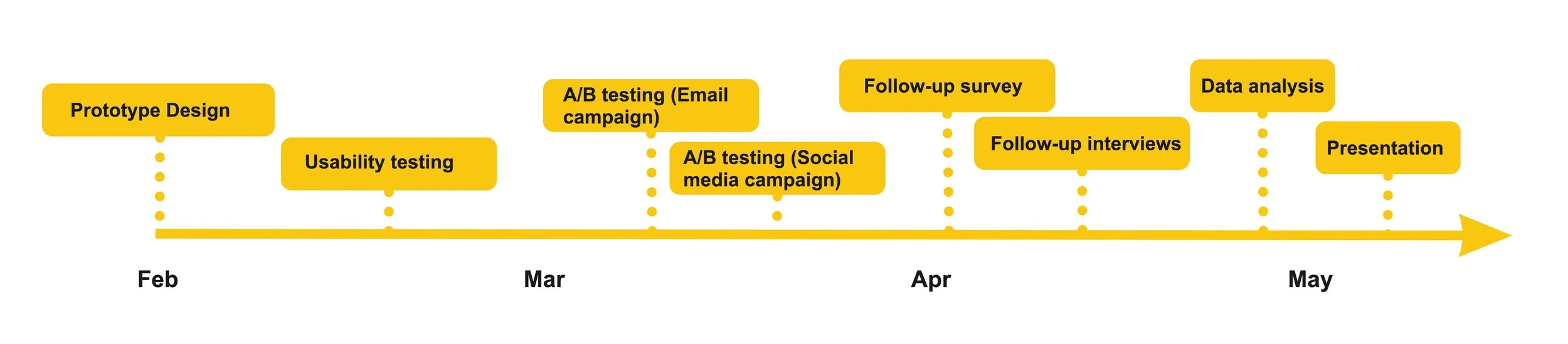
Feb.2022 - May.2022
Project Type
Evaluative Research
Design methods
Usability testing, A/B testing, follow-up survey, follow-up interviews
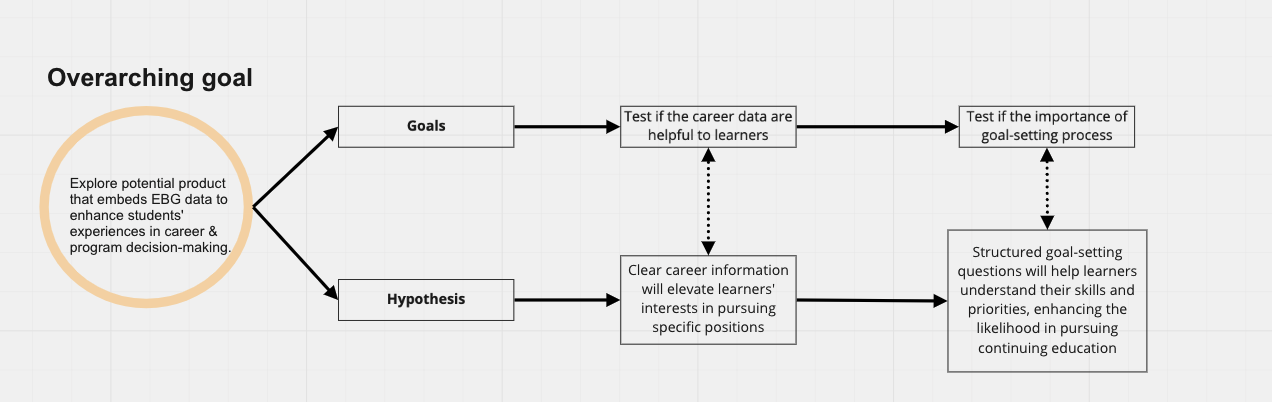
Key research goals
Identify needs, motivations and opportunities to inform the product design strategy for the career guidance page
Evaluate the usability of the current career guidance page
Understand users’ goal-setting processes when they make career decisions
Research process
Evaluative research timeline
Usability testing
Purpose: we want to test out users’ experiences on the new prototypes (career guide version 1 & 2) and make design iterations.
A/B testing
Purpose: we designed new prototypes (Version 1 & 2) and we wanted to test whether our new versions drive a higher conversion rate compared to the control page
Process:
Email campaign: we requested an email campaign and received support from the marketing team, who sent out emails to all of the prospective students at different colleges.
Social media campaign: we conducted social media campaign by promoting WGU career pages on Facebook.
Cybersecurity Analyst career guide page — Control page
Cybersecurity Analyst career guide page — Version 1 (Require user input)
Cybersecurity Analyst career guide page — Version 2 (No user input needed)
Result: The result was statistically insignificant and the data showed that the new prototypes I created were not making an impact.
Reason analysis:
Errors in data collecting
Technical issues with iFrame: We embedded the prototypes in the web page using iFrame, and one possible reason was that the cache was not loaded for our prototype, so the analytics could not catch the population
Facebook internal metrics
Facebook has an automatic optimization algorithm that it favored 1 link over the others, causing an unequal distribution of the link among random users
Design decisions were in the wrong direction
Too many variables between the control and new pages
Too much user input in the new prototype
The segmented structure of the form (survey) could potentially lose users
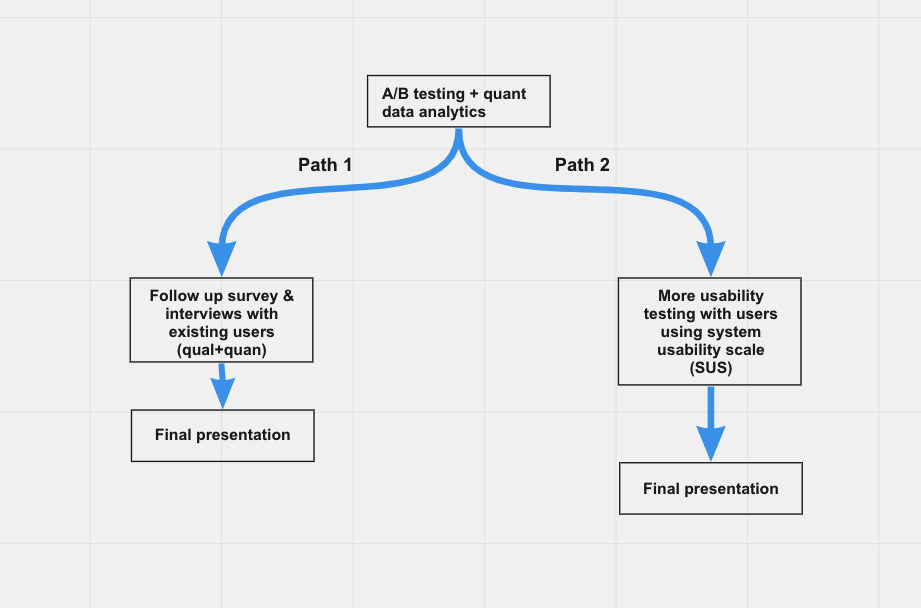
Pivoting & Decision-making
Even though the result was insignificant for the A/B testing, there are 2 paths we could pursue to reach our research goals
I made the decision of choosing path 1 due to the reasons below:
We already conducted the usability testing when testing our prototypes
A system usability scale can help us find out which page is more popular among users, but our goal is to understand the reasons behind users’ choices and their goal-setting process. Qualitative methods like interviews or think-aloud will drive us to reach the goal.
We can generate richer insights with the combination of qualitative and quantitative methods.
Follow-up surveys and interviews
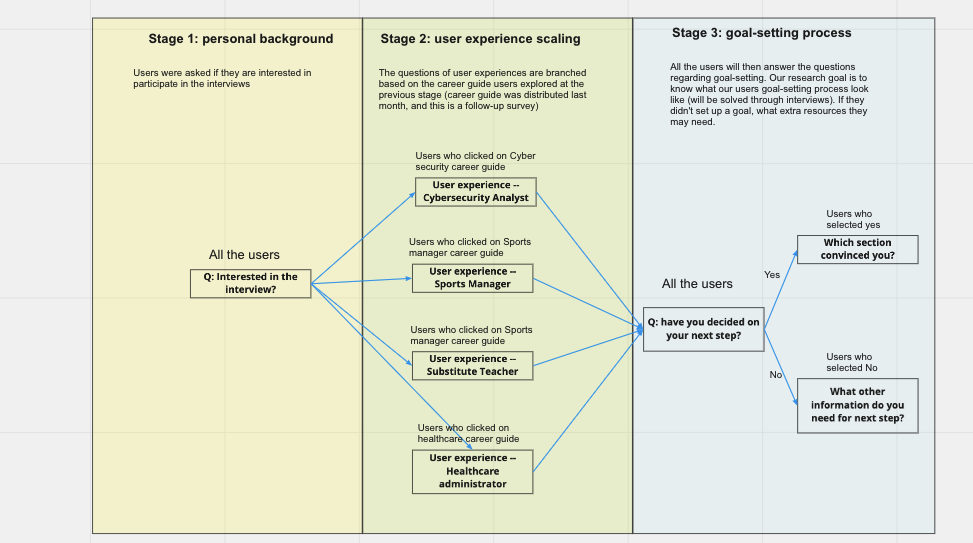
Later, we continued our study with follow-up surveys and interviews. I designed the survey via Qualtrics and received responses from over 1,200 participants. The participants were the users who have clicked on one of the career guide pages above.
Survey logic
Interview invitations were sent out to users who browsed different versions of career pages, and those under various career tracks. User Interviews were conducted among the users who opted-in for an interview during the survey. In this way, we make sure that the users had reviewed our career pages before the interviews.
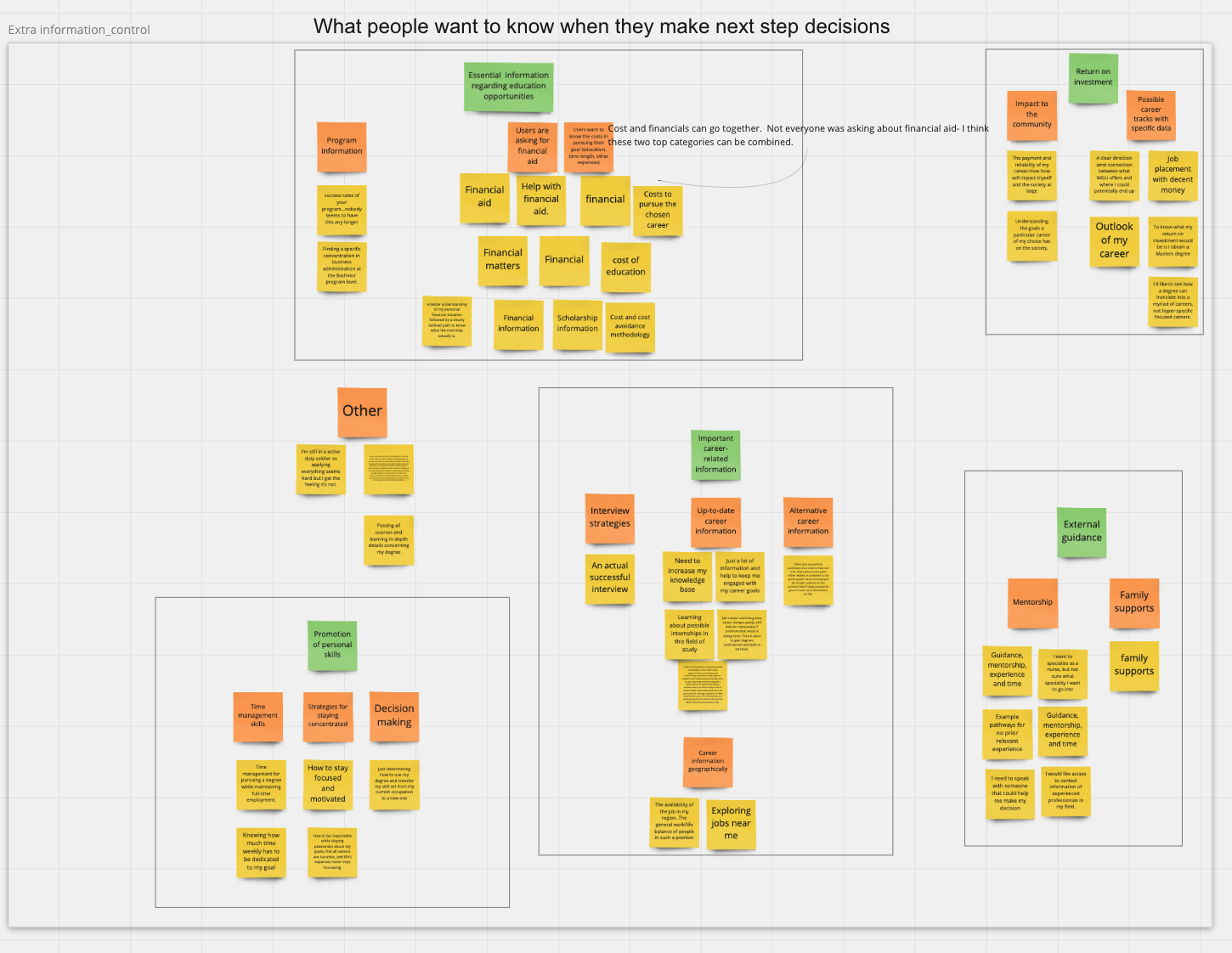
Qualitative analysis on what career information users need when they look through career guide pages
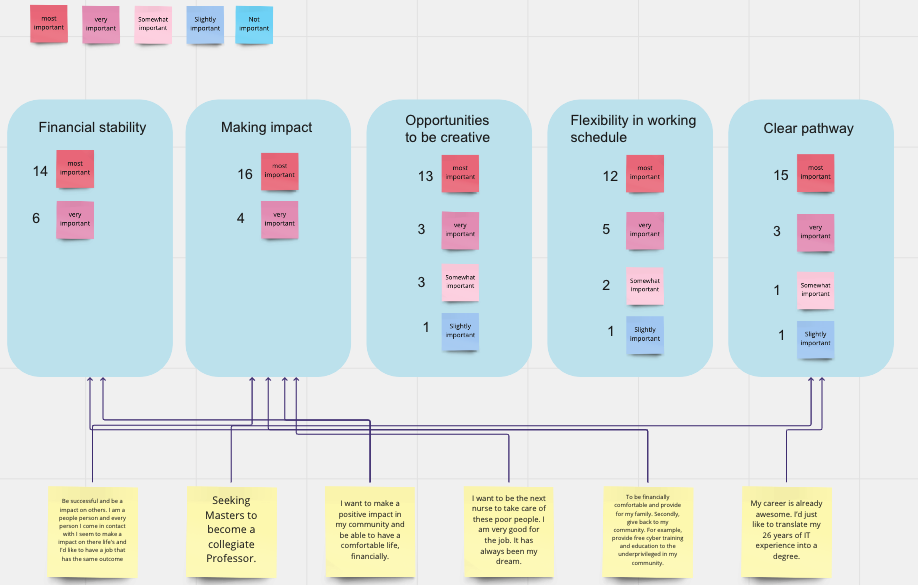
Qualitative analysis on what impact users’ goal setting process
Insights with design implications
Insight 1: Users require external guidance in decision making and other skills in order to reach the goal
Implication: extra career resources & mentorship
Insight 2:When setting a career goal, users have the most desire to learn about return on investment, including future impact and decent salary
Implication: career pathway examples
Research Impact
Increase user satisfaction rate on career guide
Inform future product decision
Increase client's customer retention rate